Sciatica

 Alternative Names: Neuropathy – sciatic nerve; Sciatic nerve dysfunction
Alternative Names: Neuropathy – sciatic nerve; Sciatic nerve dysfunction
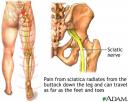
Definition: Sciatica is a condition involving pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg. It is caused by injury to or compression of the sciatic nerve.
Causes: Sciatica is a form of peripheral neuropathy. It occurs when there is damage to the sciatic nerve, located in the back of the leg. This nerve controls the muscles of the back of the knee and lower leg and provides sensation to the back of the thigh, part of the lower leg and the sole of the foot. Incomplete damage to the sciatic nerve may appear identical to damage to one of the branches of the sciatic nerve (tibial nerve dysfunction or common peroneal nerve dysfunction).
The sciatic nerve is commonly injured by fractures of the pelvis, gunshot wounds, or other trauma to the buttocks or thigh. Prolonged sitting or lying with pressure on the buttocks may also injure it. Systemic diseases, such as diabetes, can typically damage many different nerves, including the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve may also be harmed by pressure from masses such as a tumor or abscess, or by bleeding in the pelvis.
Symptoms
Sensation changes
- Of the back of the calf or the sole of the foot
- Numbness, decreased sensation
- Tingling, burning sensation
- Pain, may be severe
- Abnormal sensations
Weakness of the knee or foot
- Difficulty walking
- Inability to move the foot (in severe cases)
- Inability to bend the knee (in severe cases)
After examination there may be a need to perform additional tests. The following diagnostic tests may be performed: MRI of the lumbar spine, X-rays, blood tests, EMG/ Nerve condiuction tests.
Treatment will depend on the source and severity of the pain and may include pain medications, physical therapy, exercise program, nerve blocks or surgery.

